| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.05 - 1.15 | 0.15 - 0.65 | 0.15 - 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 3.50 - 4.25 | 9.0 - 10.00 | 0.95 - 1.35 |
Virat Special Steels is the biggest Supplier & Stockiest of DIN 1.3247 Steel.
Din 1.3247 is an excessive-carbon, excessive-pace steel founded on molybdenum. Characterized by excessive put on resistance, red hardness and durability. For this reason of its low vanadium content, this grade reveals excellent grind ability.
This grade is most often used for die-sinking cutters, milling cutters and engraving machines together with gravers as good as for device bits in automatic lathes. Also suitable for non-reducing shaping (e.g. Cold extrusion rams and instruments employed in machining substances for the aviation industry equivalent to titanium alloys).
A general-purpose high-speed steel of the molybdenum type, M2/DIN 3247/AISI M42 steel has balanced toughness, wear-resistance, and red hardness characteristics. This grade is frequently used in cold work punches, dies, and high-speed, light-cutting applications. Group M steels make up over 95% of the high-speed steels produced in the US. Except for M6, all varieties of molybdenum high-speed steels from M1 to M10 contain tungsten. These steels do not contain any cobalt at all. Tools constructed of this type of steel can be coated with titanium nitride, titanium carbide, and several other materials using a physical vapor deposition technique to increase their functionality and durability.
Virat Special Steels is the largest stockiest and supplier of DIN 3247 Steel in flat, square and round bar. We provide steel in all sizes as your requirements. DIN 3247 die steel is available in flat, square and round shape. Consult our team who will assist you for DIN 3247 steel query.

High-carbon, high-speed steel based on molybdenum. Characterized by high wear resistance, red hardness and toughness. As a result of its low vanadium content, this grade exhibits good grindability.
| Impact Toughness | 13.6 J -24 J |
| Hardness | 65.8 HRC |
| Modulus of elasticity | 190-210 GPa |
These physical properties are approximate values and can vary depending on the specific composition , heat treatment and manufacturing processes used for M42/DIN 3247/AISI M42 steel.
| Density | 8.14 g/cm3 |
| Machinability | 35% -40% of 1 % Carbon steel |
| Thermal conductivity | 27.187 W/m °C |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 11.8 x 10-6/°C |
The form and size of each component, as well as other external elements, will affect the heat treatment process, which includes the kind of furnace, quenching media, workpiece transfer facilities, and the heating temperatures including the rate of heating, cooling, and soaking durations.
Transfer the M42 to the high-temperature salt bath or furnace after preheating it to 820-870°C. Depending on the type of work being treated, the specific hardening temperature for M42/DIN 3247/AISI M42 should be in the range of 1160–1180°C in salt or 1180–1190°C in atmosphere or vacuum furnaces. After a little time at the hardening temperature, quench the component immediately in heated oil or salt at 540–595°C.
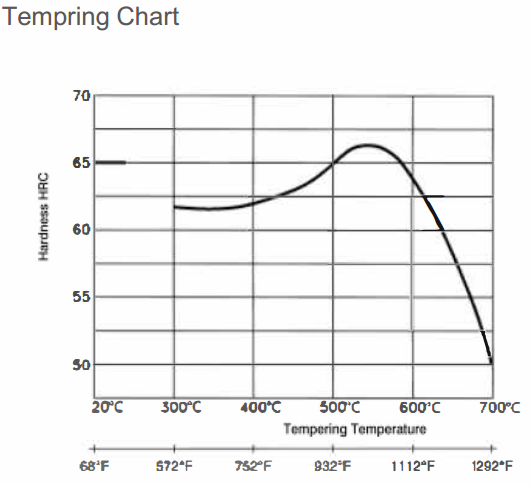
Temper immediately after quenching in a range of (510-600°C). Triple tempering is advised, with at least two hours at temperature per cycle. Between tempering treatments, the component should be cooled to room temperature in still air.
| Temperature-°C | 500 | 550 | 600 |
| Hardness - HRC | 67 | 69 | 63 |
Slowly and evenly heat the M42/DIN 3247/AISI M42 high-speed steel to 650–760 °C, then equalize. The temperature will then rise more quickly to 1010–1150°C, the forging temperature, and equalize before forging. Keep the forging temperature above 980°C; if it does, reheating will be required. After forging, high-speed steel should always be cooled down extremely slowly.
It is recommended to stress relief after machining and prior to hardening to minimize the possibility of distortion. To stress relieve heat the component to 600-650°C and soak well (approx 2 hours) Cool slowly in the furnace. Before heat treatment M42/DIN 3247/AISI M42 tools can be finished machined.
M42/DIN 3247/AISI M42 steel is a high-speed steel that is frequently not annealed in the traditional sense because of its high alloy and carbon content. Rather, it undergoes a different heat-treating process called "soft annealing" or "subcritical annealing." When M42 steel is "soft annealed," it is heated to a temperature below its critical point, often between 800-850°C (1472-1562°F), and kept there for at least two hours for every 25 mm of thickness. The furnace slowly cools down. The M42 should have an annealed hardness of no more than 269 Brinell.
M42/DIN 3247/AISI M42 should not be normalized.
Weld preheat / post-heat and interpass temperatures should be between 950 and 1050 degrees Fahrenheit. Make sure that the welding temperature does not exceed 1000 degrees Celsius (537 degrees Fahrenheit). After cooling to 400F (200C), temper at 1000F per hour/inch.
| Soft annealing °C | Cooling | Hardness HB |
|---|---|---|
| 820 - 860 | Furnace | max. 277 |
| Stress-relief annealing °C | Cooling |
|---|---|
| 630 - 650 | Furnace |
| 1st pre-heating °C | 2nd and 3rd | Hardening °C | Quenching | Tempering °C | Hardness after Teperature HRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| up to approx. 400 in an air-circulating furnace | 850 and 1050 | 1160-1190 | Saltbath, at least 550 °C Oil ,Air | at least twice 550-560 | 66 – 69 |
1 For cold-forming tools with a complex geometry, a hardening temperature at the lower end of the quoted range is recommended. The stated hardening temperatures apply to saltbath hardening only. For vacuum hardening, we suggest a reduction of 10 °C to 30 °C.
For tools subject to severe mechanical wear (e.g. in case of small cross-section cuts at high cutting speeds). Particularly suitable for die-sinking cutters, milling cutters and engraving machines including gravers as well as for tool bits in automatic lathes. Also suitable for non-cutting shaping (e.g. cold extrusion rams and tools employed in machining materials for the aviation industry such as titanium alloys).